Overview of Asset Allocation Strategies
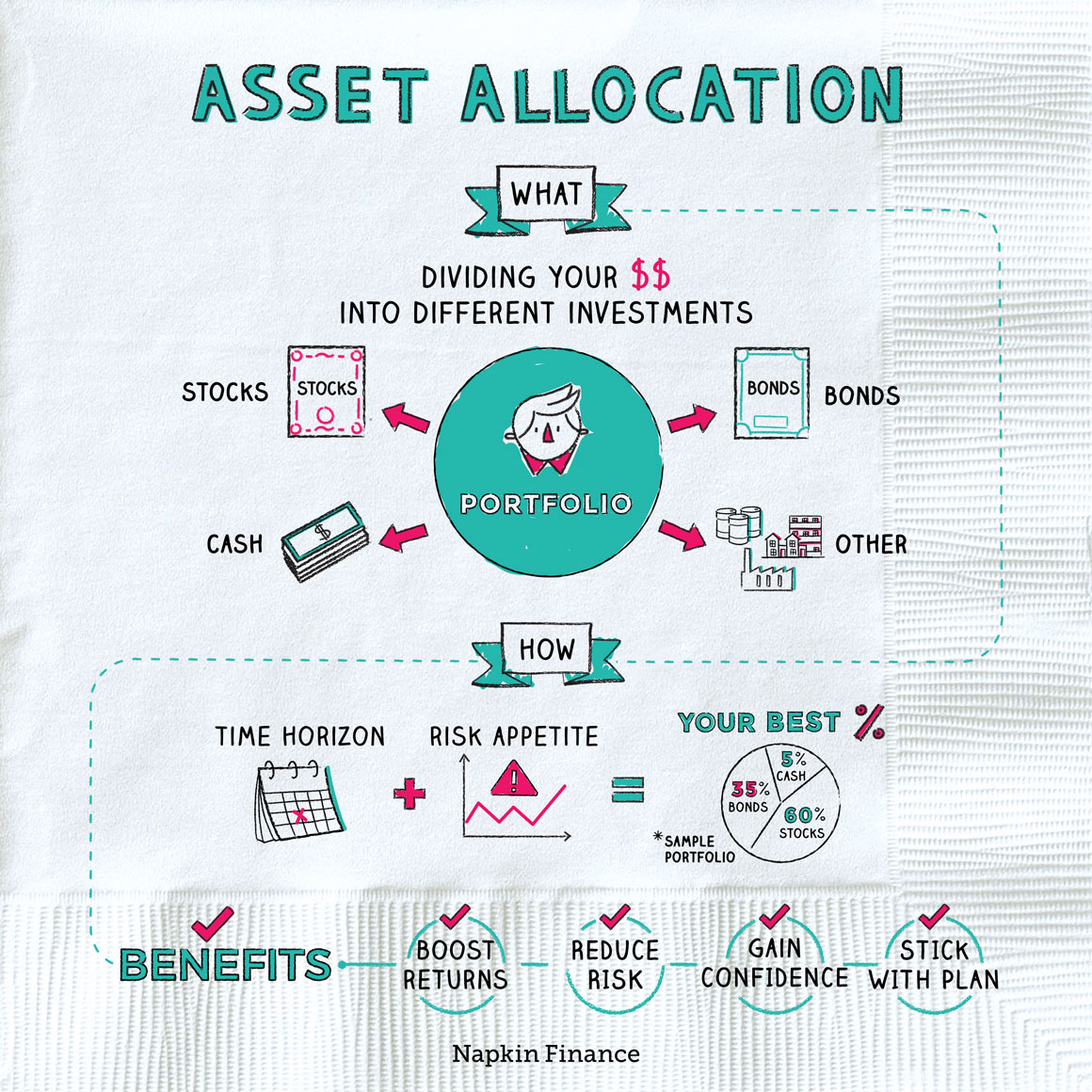
Asset allocation is a crucial component of investment portfolios, involving the distribution of investments across various asset classes such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents. This strategy aims to optimize returns while managing risks by diversifying investments.
Key Objectives of Asset Allocation Strategies
- Maximize Returns: Asset allocation aims to achieve the highest possible return on investments given a certain level of risk tolerance.
- Minimize Risk: By diversifying investments across different asset classes, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility on their portfolios.
- Achieve Financial Goals: Asset allocation strategies are designed to help investors reach their financial objectives, whether it’s retirement savings, wealth preservation, or capital growth.
- Maintain Liquidity: Balancing investments in liquid assets ensures that investors have access to funds when needed, without compromising long-term goals.
Benefits of Diversification in Asset Allocation
Diversification plays a crucial role in asset allocation strategies by spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions. This approach helps mitigate the risk of significant losses in any single investment. By diversifying, investors can potentially increase returns while reducing overall portfolio volatility. It also allows for exposure to a wider range of opportunities, capturing growth potential in various sectors and markets.
Types of Asset Classes
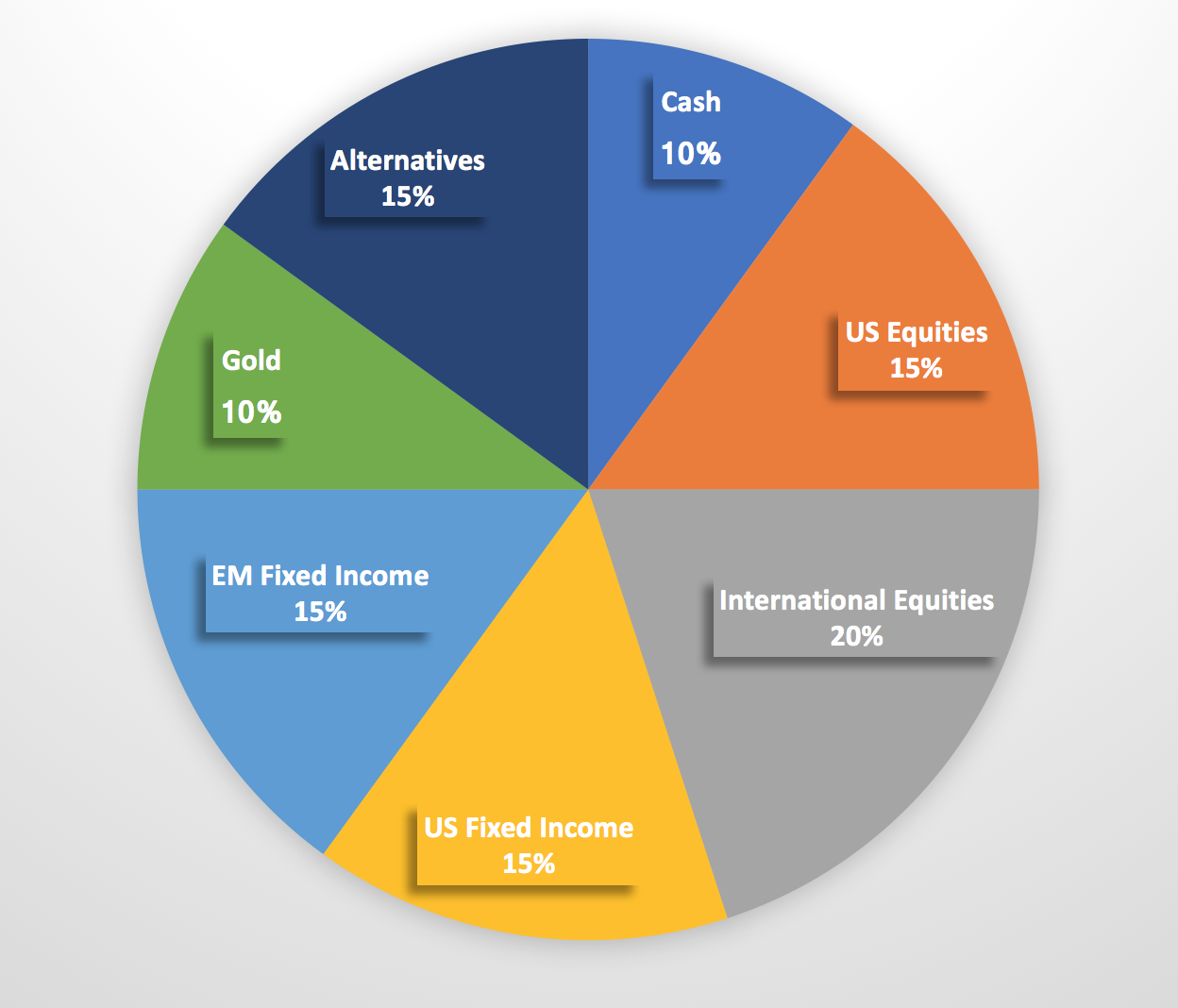
Investors often allocate their assets across different classes to diversify their portfolio and manage risk. Here are some common asset classes used in asset allocation:
1. Equities
Equities represent ownership in a company and are also known as stocks. They have the potential for high returns but come with higher risk due to market volatility. Equities can include large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap stocks, as well as international stocks. They can contribute to portfolio growth and provide dividends.
2. Fixed Income
Fixed income securities, such as bonds, represent debt owed by an entity. They are considered lower risk compared to equities and provide regular interest payments. Bonds can include government, corporate, municipal, and treasury bonds. They contribute to income generation and stability in a portfolio.
3. Real Estate
Real estate investments involve properties such as residential, commercial, or industrial real estate. They can provide rental income and potential appreciation. Real estate investment trusts (REITs) are a popular way to invest in real estate without owning physical properties. Real estate can add diversification and inflation protection to a portfolio.
4. Commodities
Commodities include physical goods such as gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products. They can act as a hedge against inflation and currency fluctuations. Commodities can provide diversification and risk mitigation in a portfolio.
5. Cash Equivalents
Cash equivalents are low-risk, highly liquid assets such as certificates of deposit (CDs), money market funds, and Treasury bills. They offer stability and capital preservation in a portfolio. Cash equivalents provide liquidity and can be used for short-term needs.
6. Alternative Investments
Alternative investments cover a wide range of assets beyond traditional classes, including private equity, hedge funds, venture capital, and cryptocurrencies. They can offer diversification, uncorrelated returns, and potential higher yields. Alternative investments can add complexity and risk-return opportunities to a portfolio.
These asset classes each have unique risk-return profiles and characteristics that investors consider when constructing a diversified portfolio. By allocating assets across different classes, investors aim to achieve their financial goals while managing risk effectively.
Traditional Asset Allocation Strategies
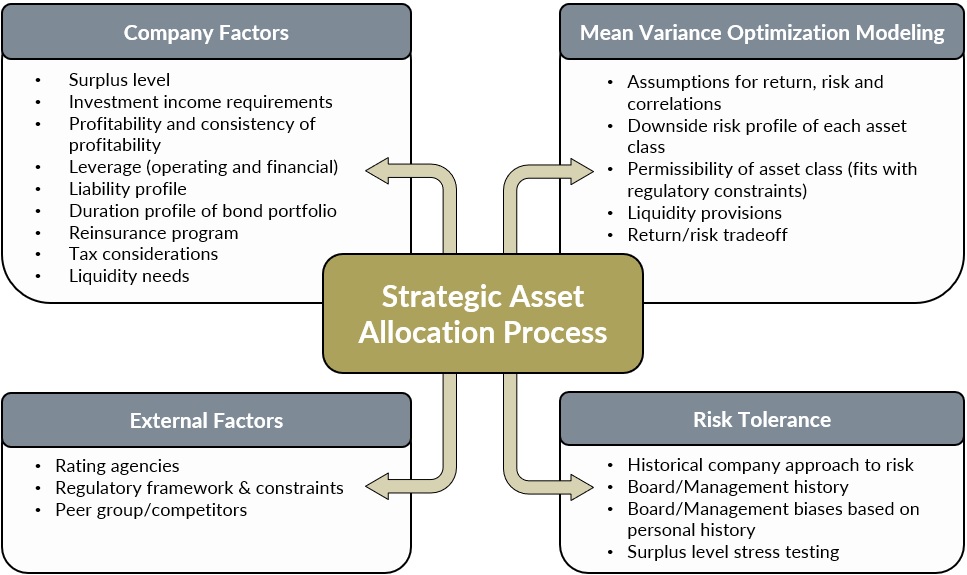
Asset allocation strategies have evolved over time, with traditional approaches laying the foundation for modern portfolio management. These strategies are based on theories and principles that have stood the test of time, providing investors with a framework to build their portfolios.
Modern Portfolio Theory Impact
Modern Portfolio Theory, developed by Harry Markowitz, revolutionized the way investors approach asset allocation. By emphasizing the importance of diversification and the relationship between risk and return, this theory has become a cornerstone of traditional asset allocation strategies. Investors now focus on constructing portfolios that optimize risk-adjusted returns by combining assets with different correlations.
Strategic Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation is a long-term approach that involves setting target allocations for different asset classes based on an investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals. This strategy aims to maintain a consistent portfolio mix over time, periodically rebalancing to realign with the target allocations. By staying committed to the strategic plan, investors can benefit from the power of compounding and weather market fluctuations.
Strategic vs. Tactical Asset Allocation
Strategic asset allocation differs from tactical asset allocation in its focus and approach. While strategic asset allocation sets a long-term plan and sticks to it, tactical asset allocation involves making short-term adjustments based on market conditions or forecasts. Tactical allocation aims to capitalize on short-term opportunities or manage risks, deviating from the target allocations set in the strategic plan. Both approaches have their merits, and some investors may choose to combine elements of both strategies in their portfolio management.
Alternative Asset Allocation Strategies
Alternative asset allocation strategies play a crucial role in diversifying investment portfolios and managing risk. One such strategy is dynamic asset allocation, which involves adjusting the allocation of assets based on changing market conditions.
Dynamic Asset Allocation
Dynamic asset allocation involves actively managing the allocation of assets in a portfolio to capitalize on market opportunities and mitigate risks. This strategy allows investors to adjust their exposure to different asset classes based on market conditions, economic outlook, and other relevant factors.
- Benefits of Dynamic Asset Allocation:
- Opportunity to capitalize on market trends and opportunities
- Ability to reduce risk by adjusting allocations based on market conditions
- Potential for higher returns by actively managing asset allocations
- Challenges of Dynamic Asset Allocation:
- Requires active monitoring and decision-making
- May involve higher transaction costs due to frequent adjustments
- Success depends on accurate market analysis and forecasting
Alternative Asset Classes
Alternative asset classes are non-traditional investments that can provide diversification benefits and unique return opportunities. Some examples of alternative asset classes include:
| Asset Class | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) | Provide exposure to real estate markets without direct ownership |
| Commodities | Offer inflation protection and diversification benefits |
| Private Equity | Investments in private companies with growth potential |
| Hedge Funds | Seek to generate returns in various market conditions |