Overview of Capital Gains Tax Rates

Capital gains tax rates refer to the tax imposed on the profits from the sale of assets such as stocks, real estate, or other investments. These rates can vary depending on the type of asset sold, the holding period of the asset, and the individual’s income level.
Types of Capital Gains Tax Rates
- Short-term Capital Gains Tax: This tax is applied to profits made from the sale of assets held for one year or less. Short-term capital gains are typically taxed at the individual’s ordinary income tax rate.
- Long-term Capital Gains Tax: Long-term capital gains apply to assets held for more than one year before being sold. These gains are usually taxed at lower rates than short-term gains, ranging from 0% to 20% based on the individual’s income.
Factors Affecting Capital Gains Tax Rates
- Income Level: Higher-income individuals may be subject to higher capital gains tax rates compared to those in lower tax brackets.
- Holding Period: The length of time an asset is held before being sold can impact the tax rate, with longer holding periods often resulting in lower tax rates.
Current Capital Gains Tax Rates
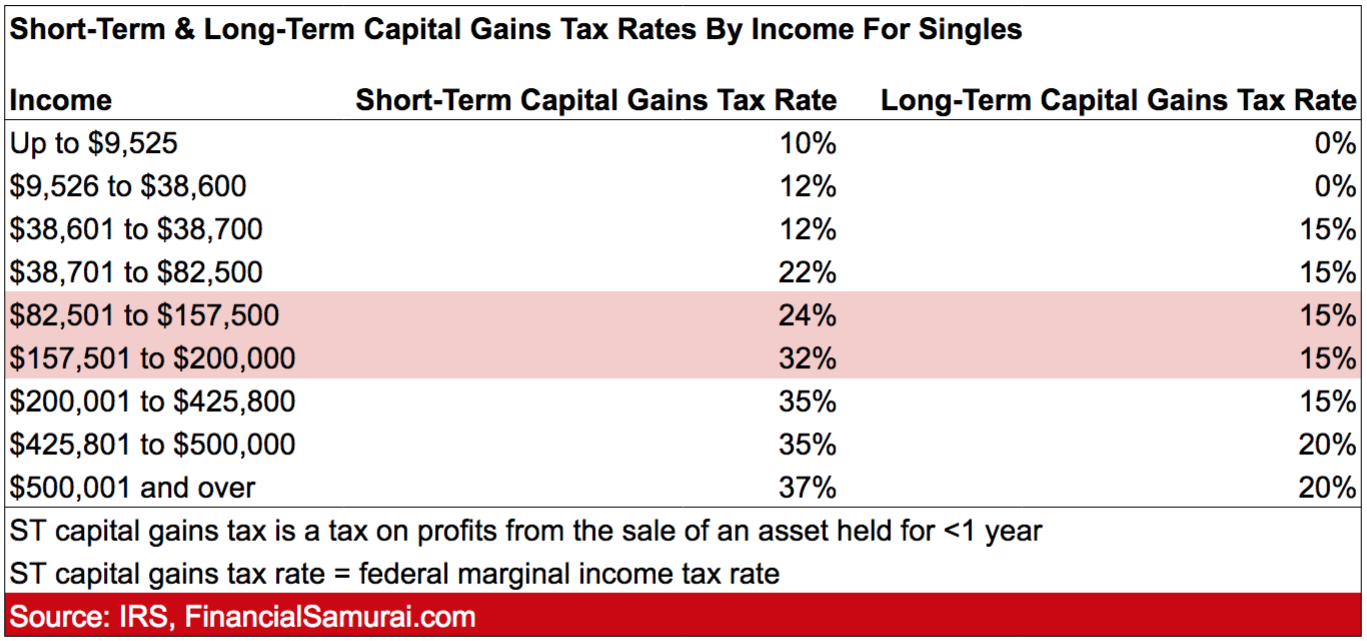
Currently, the capital gains tax rates vary depending on whether the gains are classified as short-term or long-term. Short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates, while long-term capital gains are subject to lower tax rates.
Comparison of Tax Rates for Different Types of Assets
When it comes to different types of assets, such as stocks, real estate, and collectibles, the tax rates can vary. Here is a comparison:
- Stocks: Long-term capital gains on stocks are typically taxed at a lower rate than short-term capital gains. The specific rate depends on your income level.
- Real Estate: Real estate capital gains tax rates also differ for short-term and long-term gains. Like stocks, long-term gains are usually taxed at a lower rate.
- Collectibles: Collectibles, such as art or antiques, are subject to a higher capital gains tax rate compared to other assets. The rate can be as high as 28% for long-term gains.
Recent Changes in Capital Gains Tax Rates
There have been discussions about potential changes to capital gains tax rates, including proposals to increase the tax rate on long-term capital gains for high-income individuals. It is essential to stay informed about any upcoming changes that could impact your investment decisions.
Impact of Capital Gains Tax Rates

Capital gains tax rates play a crucial role in influencing investment decisions and shaping the overall economic landscape. Let’s delve into how these rates impact various aspects of the financial world.
Effect on Investment Decisions
Capital gains tax rates can significantly influence the investment choices made by individuals and businesses. When tax rates are high, investors may be more hesitant to realize their gains by selling assets, as they would have to pay a larger portion in taxes. On the other hand, lower tax rates can incentivize investors to take risks and invest in assets that have the potential for higher returns.
Economic Implications of High or Low Rates
The level of capital gains tax rates can have profound economic implications. High tax rates may discourage investment and entrepreneurship, leading to slower economic growth. Conversely, lower tax rates can stimulate investment, spur innovation, and fuel economic expansion. Finding the right balance is essential to promote economic prosperity while ensuring fair taxation.
Historical Examples
Historically, changes in capital gains tax rates have had notable impacts on financial markets. For instance, when tax rates were reduced in the past, there was often a surge in market activity as investors sought to take advantage of the more favorable conditions. Conversely, increases in tax rates have sometimes led to market downturns as investors adjusted their strategies in response to the new tax environment.
Strategies to Minimize Capital Gains Tax
When it comes to minimizing capital gains tax, there are several strategies that individuals can utilize to reduce their tax liability and maximize their investment returns.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy used to offset capital gains by selling investments that have incurred a loss. By realizing these losses, investors can reduce their overall capital gains tax liability. It involves strategically selling losing investments to offset gains and potentially reduce taxable income.
Tax-Advantaged Accounts
One effective way to minimize capital gains tax is by utilizing tax-advantaged accounts such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s. These accounts offer tax benefits that can help investors grow their savings while minimizing their tax burden. Contributions to these accounts are often tax-deductible, and the investments grow tax-deferred until withdrawal, allowing individuals to potentially avoid or minimize capital gains tax.