Introduction to International Stock Investing
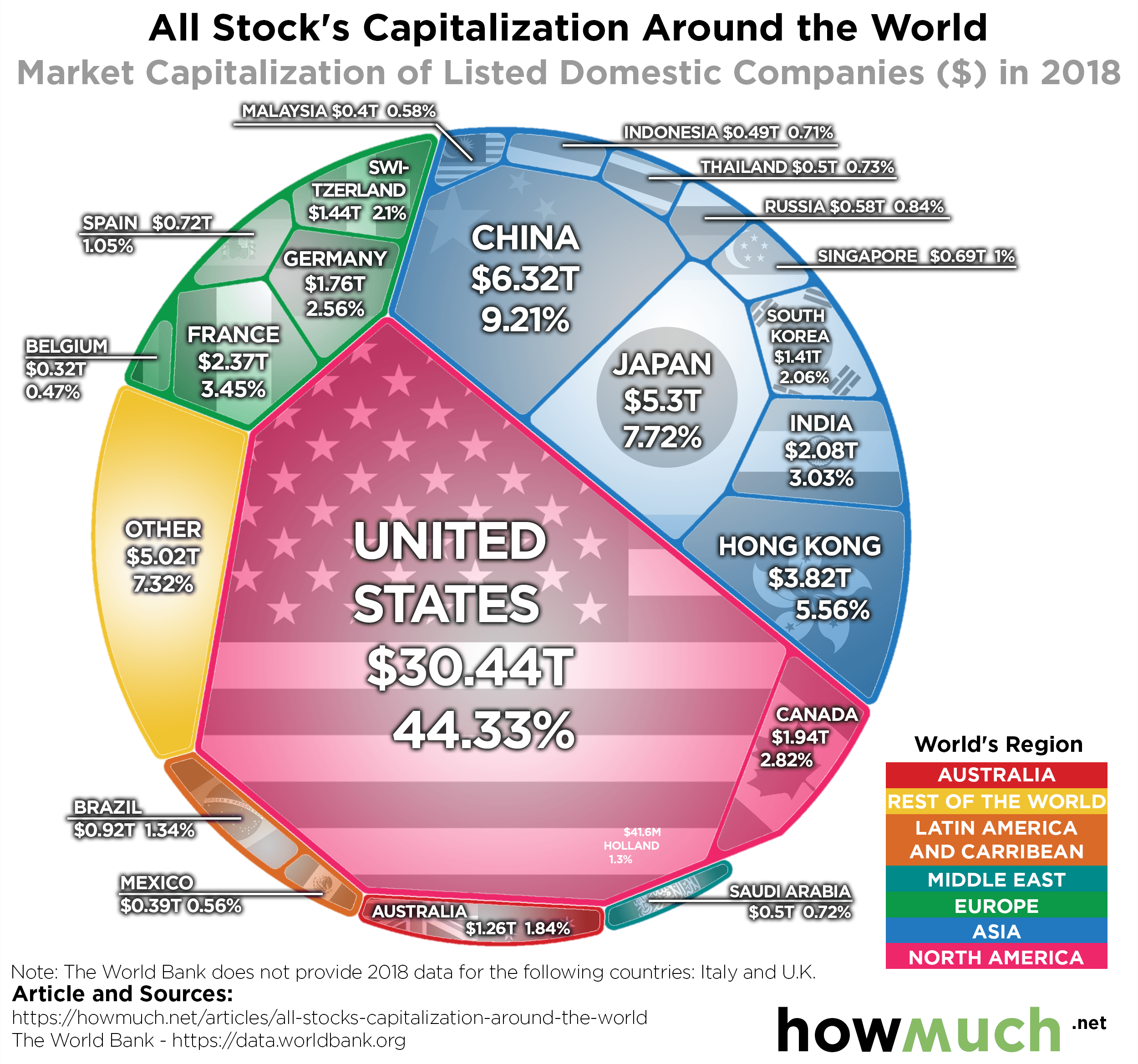
International stocks refer to investments in companies that are based outside of your home country. Including international stocks in a diversified portfolio is essential to reduce risk and increase potential returns.
Benefits of Investing in International Stocks
- Diversification: Investing in international stocks helps spread risk across different economies and industries, reducing the impact of market fluctuations in one country.
- Exposure to Growth Opportunities: International markets offer access to industries and regions experiencing rapid growth that may not be available in domestic markets.
- Currency Diversification: Investing in international stocks allows you to diversify currency exposure, which can act as a hedge against the depreciation of your home currency.
Risks Associated with Investing in International Markets
- Political and Economic Instability: International markets may be subject to political unrest, government policies, or economic challenges that can impact the performance of investments.
- Currency Risk: Fluctuations in exchange rates can affect the value of international investments when converted back to your home currency.
- Regulatory Differences: Each country has its own set of rules and regulations governing investments, which can create uncertainty and risk for international investors.
Researching International Stocks

Researching international stocks is crucial for making informed investment decisions. By understanding the various factors that can impact the performance of international companies and markets, investors can mitigate risks and identify potential opportunities.
Strategies for Researching International Companies and Markets
- Utilize financial statements and annual reports to assess the financial health of the company.
- Stay updated on global economic trends and market conditions that may affect international investments.
- Consider cultural and social factors that could impact the success of the company in different regions.
- Consult with financial advisors or experts with knowledge of specific international markets.
Analyzing Political and Economic Factors in International Investments
- Monitor political stability in countries where you are considering investing to gauge potential risks.
- Assess the impact of government policies and regulations on the company’s operations and profitability.
- Analyze economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment levels to evaluate the overall economic environment.
Understanding Currency Exchange Rates in International Stock Investing
-
Fluctuations in currency exchange rates can significantly impact the returns on international investments.
- Consider hedging strategies to mitigate currency risk and protect your investment portfolio.
- Stay informed about geopolitical events and economic developments that could influence currency movements.
Investing Strategies for International Stocks
When it comes to investing in international stocks, there are different strategies that investors can employ to achieve their financial goals. Two common approaches are passive and active investment strategies, each with its own set of advantages and considerations.
Passive investment strategies involve investing in a diversified portfolio of international stocks and holding them for the long term, without actively buying or selling based on market conditions. This approach aims to match the performance of a broad market index, such as the MSCI World Index, rather than trying to outperform it. Passive strategies are often associated with lower costs and less frequent trading compared to active strategies.
On the other hand, active investment strategies involve actively managing a portfolio of international stocks to outperform the market. This can involve extensive research, market analysis, and frequent trading to capitalize on short-term market opportunities. While active strategies have the potential for higher returns, they also come with higher costs and risks, as well as the challenge of consistently beating the market.
Role of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) in International Stock Investing
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) play a significant role in international stock investing by providing investors with a convenient way to gain exposure to a diversified portfolio of international stocks. ETFs are investment funds that are traded on stock exchanges, similar to individual stocks, and typically track specific market indexes or sectors.
One of the key advantages of ETFs is their low cost compared to actively managed mutual funds. ETFs also offer liquidity, transparency, and flexibility, allowing investors to easily buy and sell shares throughout the trading day. Additionally, ETFs provide exposure to international markets without the need to directly invest in individual foreign stocks, making them a popular choice for investors looking to diversify their portfolios globally.
Sector Diversification in International Markets
When investing in international markets, sector diversification is essential to mitigate risks and maximize returns. Sector diversification involves spreading investments across different industries and sectors, such as technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods, to reduce the impact of market fluctuations on a portfolio.
By diversifying across sectors, investors can potentially benefit from the growth of multiple industries while reducing the impact of downturns in any single sector. This approach helps balance the overall risk and return profile of a portfolio, making it more resilient to economic changes and sector-specific challenges.
Overall, incorporating sector diversification strategies into international stock investing can help investors build a well-rounded portfolio that is better positioned to weather market volatility and capitalize on global opportunities.
Managing Risks in International Stock Investing
When investing in international stocks, it is crucial to consider and manage the various risks that come with it. Geopolitical risks, currency fluctuations, and global events can all impact your investments. Here, we will discuss how to identify and mitigate these risks.
Geopolitical Risks Impacting International Investments
Geopolitical risks refer to factors such as political instability, conflicts, and regulatory changes in foreign countries that can affect the performance of international stocks. It is essential to stay informed about the political landscape of the countries you are investing in and assess how these factors may impact your investments.
- Monitor political developments: Stay updated on news and events that could potentially affect the countries where you have investments.
- Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across different countries and industries to reduce the impact of any geopolitical risks on your overall portfolio.
- Consider investing in stable economies: Countries with strong institutions and stable political environments may offer a lower level of geopolitical risk.
Hedging Currency Risk in International Stock Investing
Currency risk arises from fluctuations in exchange rates, which can impact the value of your investments when you are investing in foreign markets. Here are some strategies to hedge against currency risk:
- Use currency hedging instruments: Invest in currency futures, options, or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that are designed to protect against currency fluctuations.
- Diversify currency exposure: Hold investments in various currencies to offset the impact of currency fluctuations on your portfolio.
- Consider investing in multinational companies: Companies that have operations in multiple countries may be less affected by currency fluctuations.
Impact of Global Events on International Stock Markets
Global events such as economic crises, natural disasters, or pandemics can have a significant impact on international stock markets. To mitigate risks associated with global events, consider the following:
- Stay informed: Keep track of global news and events that could potentially affect the financial markets.
- Review your portfolio: Regularly assess your investments and make adjustments based on changing global conditions.
- Focus on long-term goals: Maintain a long-term perspective when investing in international stocks to ride out short-term market fluctuations caused by global events.
Emerging Markets vs. Developed Markets
When it comes to investing in international stocks, one crucial consideration is whether to focus on emerging markets or developed markets. Each type of market offers unique opportunities and risks for investors to navigate.
Emerging markets are countries with rapidly growing economies and industries, such as Brazil, China, India, and South Africa. These markets have the potential for high returns due to their growth prospects, but they also come with higher risks. Factors such as political instability, currency fluctuations, and less developed regulatory frameworks can make investing in emerging markets more volatile.
On the other hand, developed markets like the United States, Japan, and Germany are more stable and have well-established regulatory systems. While the growth potential in developed markets may not be as high as in emerging markets, they offer a lower level of risk for investors. These markets are often seen as safer havens during times of global economic uncertainty.
Growth Potential and Risks in Emerging Markets
Emerging markets offer the potential for high growth due to factors like expanding middle-class populations, increasing consumer spending, and rapid industrialization. Investors in emerging markets can benefit from accessing industries and companies that are at an early stage of development, potentially leading to significant returns on investment.
However, investing in emerging markets also comes with risks such as political instability, currency devaluation, and liquidity issues. Investors need to carefully assess these risks and be prepared for higher levels of volatility compared to investing in developed markets.
Regulatory Environment in Emerging Markets vs. Developed Markets
The regulatory environment in emerging markets can be less stringent and more prone to changes compared to developed markets. This can create challenges for investors in terms of compliance, transparency, and corporate governance. Understanding the regulatory landscape in each market is crucial for investors to make informed decisions and mitigate risks.
In contrast, developed markets typically have well-established regulatory frameworks that provide a more stable and predictable environment for investors. These markets offer greater transparency, investor protection, and adherence to international standards, making them more attractive for risk-averse investors looking for stability in their portfolio.