Overview of Stock Options
Stock options are financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific amount of a stock at a predetermined price within a set timeframe. They are often used as a way to speculate on the price movement of a stock or as a form of employee compensation.
Types of Stock Options
- Non-Qualified Stock Options: These are typically offered to employees as part of their compensation package and are subject to taxation upon exercise.
- Incentive Stock Options: These are usually offered to executives and key employees and can have tax advantages if certain conditions are met.
- Exchange-Traded Options: These are standardized contracts traded on exchanges that allow investors to speculate on stock price movements without owning the underlying stock.
Comparison to Other Investment Vehicles
- Stock options offer leverage, allowing investors to control a larger position with less capital compared to buying stocks outright.
- Unlike stocks, options have an expiration date, which means they are time-sensitive and can lose value as time passes.
- Compared to futures contracts, options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset.
Benefits of Stock Options
Stock options offer several advantages for investors looking to diversify their portfolio and potentially maximize their returns.
Diversification
Stock options provide investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolio by gaining exposure to a wide range of companies across different sectors. By holding options on various stocks, investors can spread their risk and reduce potential losses from any single stock performing poorly.
Leverage
One of the key benefits of stock options is the ability to leverage your investment. With options, you can control a larger position in a stock for a fraction of the cost of buying the shares outright. This leverage can amplify your returns if the stock price moves in your favor.
Hedging
Stock options can also be used as a hedging tool to protect your portfolio against potential downside risk. By purchasing put options, investors can insure their holdings and limit losses in the event of a market downturn or a drop in the price of a specific stock.
Tax Benefits
Another advantage of stock options is the favorable tax treatment they can offer. In some cases, capital gains from options trading may be taxed at a lower rate compared to other forms of investment income. Additionally, certain strategies involving stock options can help investors defer taxes or minimize their tax liabilities.
Risks Associated with Stock Options
When trading stock options, there are various risks that investors should be aware of in order to make informed decisions. Understanding these risks can help mitigate potential losses and maximize profits.
Market Volatility Impact
Market volatility plays a significant role in how stock options perform. When the market is highly volatile, the prices of stocks can fluctuate drastically, leading to increased uncertainty for option holders. This can result in a higher chance of options expiring worthless or losing value rapidly.
Strategies to Mitigate Risks:
- Diversification: One way to mitigate risks associated with stock options is to diversify your portfolio. By spreading your investments across different assets, industries, or sectors, you can reduce the impact of volatility on your overall portfolio.
- Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Implementing stop-loss orders can help limit potential losses by automatically selling your options when they reach a certain predetermined price. This can protect your investment from significant downturns in the market.
- Hedging Strategies: Utilizing hedging strategies, such as buying put options or using other derivative instruments, can help offset potential losses in your stock options portfolio. These strategies can act as insurance against adverse market movements.
- Risk Management: It is essential to have a solid risk management plan in place when trading stock options. This includes setting clear investment goals, defining your risk tolerance, and regularly reviewing and adjusting your positions based on market conditions.
How to Trade Stock Options
Trading stock options involves buying and selling contracts that give you the right to buy or sell a specific stock at a set price within a certain timeframe. It can be a way to leverage your investment and potentially earn higher returns, but it also comes with risks.
Different Trading Strategies
- Buying Calls: This strategy involves purchasing call options, which give you the right to buy the underlying stock at a predetermined price before the expiration date. It is a bullish strategy used when you expect the stock price to rise.
- Buying Puts: On the other hand, buying put options gives you the right to sell the underlying stock at a specific price before the expiration date. This strategy is used when you anticipate the stock price to fall, making it a bearish approach.
- Covered Calls: This strategy involves holding a long position in a stock while selling a call option on the same stock. It can generate income if the stock price remains stable or increases slightly.
- Protective Puts: By purchasing put options for stocks you already own, you can protect your investment from potential downside risk. This strategy acts as insurance against a significant drop in stock price.
Tips for Beginners
- Educate Yourself: Before diving into trading options, make sure you understand how they work and the associated risks. Take the time to learn about different strategies and how to execute them.
- Start Small: Begin with a small investment to gain experience and minimize potential losses. As you become more comfortable with trading options, you can gradually increase your investment amount.
- Set Clear Goals: Define your trading goals and risk tolerance before making any trades. Establishing a clear plan can help you make informed decisions and avoid impulsive moves.
- Practice with Paper Trading: Consider practicing trading options without using real money through paper trading platforms. This can help you familiarize yourself with the process and test out different strategies.
Understanding Stock Option Terminology

When it comes to trading stock options, understanding the key terminology is essential for making informed decisions and maximizing profits. Let’s delve into some of the most important terms you need to know.
Call Options and Put Options
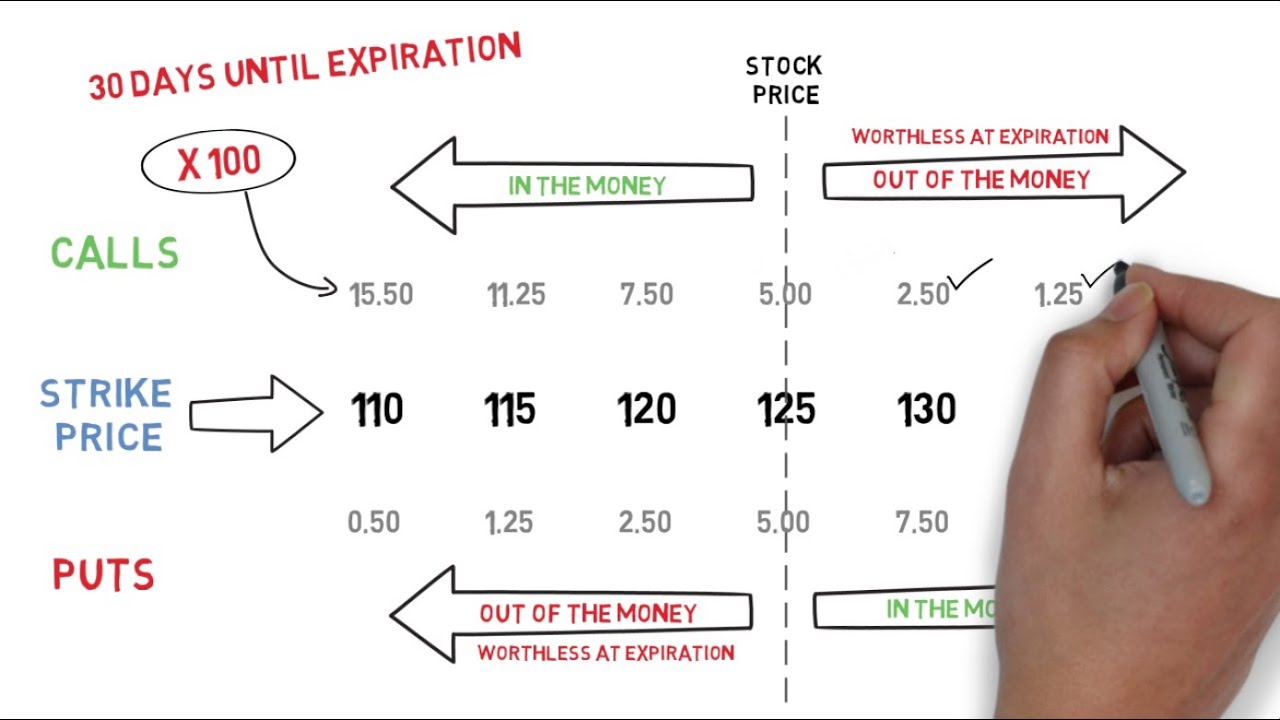
- Call Options: Call options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specified amount of a stock at a predetermined price before the option expires.
- Put Options: Put options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specified amount of a stock at a predetermined price before the option expires.
Strike Price
The strike price is the price at which the option holder can buy or sell the underlying stock if they choose to exercise the option.
Expiration Date
The expiration date is the date on which the option expires and becomes worthless if not exercised. It’s crucial to pay attention to expiration dates when trading stock options.
Intrinsic Value
The intrinsic value of an option is the difference between the current price of the underlying stock and the option’s strike price. If an option has intrinsic value, it is said to be “in the money.”
Understanding these key terms will give you a solid foundation for navigating the world of stock options trading and making informed decisions. Remember, knowledge is power in the world of finance.