Overview of Interest Rates and Mortgages
Interest rates refer to the cost of borrowing money, usually expressed as a percentage. On the other hand, mortgages are loans taken out to purchase real estate, with the property serving as collateral for the loan.
The relationship between interest rates and mortgage rates is direct and significant. Mortgage rates are influenced by the prevailing interest rates set by central banks. When interest rates are low, mortgage rates tend to be lower as well, making borrowing more affordable for homebuyers. Conversely, when interest rates rise, mortgage rates follow suit, increasing the cost of borrowing for mortgages.
How Interest Rates Affect the Cost of Borrowing for Mortgages
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the overall cost of borrowing for mortgages. Here are some key points to consider:
- Higher interest rates lead to higher monthly mortgage payments, as a larger portion of the payment goes towards interest rather than principal.
- Increasing interest rates can also reduce the amount of the loan that borrowers qualify for, making it harder to afford a home.
- Conversely, lower interest rates can result in lower monthly payments and allow borrowers to qualify for larger loan amounts.
- Changes in interest rates can impact the affordability of homes and influence the housing market’s overall health.
Factors Influencing Mortgage Interest Rates
When it comes to mortgage interest rates, several key factors play a significant role in determining the rates borrowers will pay. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions when entering the housing market.
Economic Conditions Impact
The state of the economy has a direct impact on mortgage interest rates. In times of economic growth and low unemployment rates, interest rates tend to rise. Conversely, during economic downturns or times of uncertainty, interest rates may decrease to stimulate borrowing and spending.
Role of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in setting interest rates through its monetary policy decisions. By adjusting the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight, the Fed influences borrowing costs for consumers. When the Fed raises rates, mortgage interest rates tend to follow suit. On the other hand, when the Fed lowers rates, mortgage rates may decrease, making borrowing more affordable for homebuyers.
Types of Mortgage Interest Rates
When it comes to mortgage interest rates, there are primarily two main types: fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which are important for potential homebuyers to consider before making a decision.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Fixed-rate mortgages have a set interest rate that remains constant throughout the life of the loan. This means that your monthly payments will stay the same, providing predictability and stability. One of the main advantages of a fixed-rate mortgage is that it protects you from any potential increases in interest rates, giving you peace of mind knowing that your payments will not change.
On the downside, fixed-rate mortgages typically come with higher initial interest rates compared to adjustable-rate mortgages. This means that you may end up paying more in interest over the life of the loan, especially if interest rates decrease in the future.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), on the other hand, have interest rates that can fluctuate over time based on market conditions. This means that your monthly payments can vary, potentially increasing if interest rates rise. However, ARMs often start with lower initial interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages, making them more affordable in the short term.
One of the main advantages of adjustable-rate mortgages is that they have the potential to save you money if interest rates decrease. However, they also come with the risk of higher payments if interest rates go up.
Impact of Changes in Interest Rates
Changes in interest rates affect fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages differently. For fixed-rate mortgages, once you lock in your interest rate, you are protected from any fluctuations in the market. This means that even if interest rates rise, your payments will remain the same.
On the other hand, changes in interest rates directly impact adjustable-rate mortgages. If interest rates increase, your monthly payments will go up, potentially making it more challenging to afford your mortgage. Conversely, if interest rates decrease, you may benefit from lower payments with an ARM.
Overall, choosing between a fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgage depends on your individual financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. It’s essential to carefully weigh the pros and cons of each type of mortgage before making a decision.
Mortgage Rate Trends and Forecasting
Understanding the historical trends and forecasting of mortgage interest rates is crucial for homeowners and potential buyers alike. By analyzing past data and current market conditions, we can gain insights into what factors contribute to fluctuations in mortgage rates and what to expect in the future.
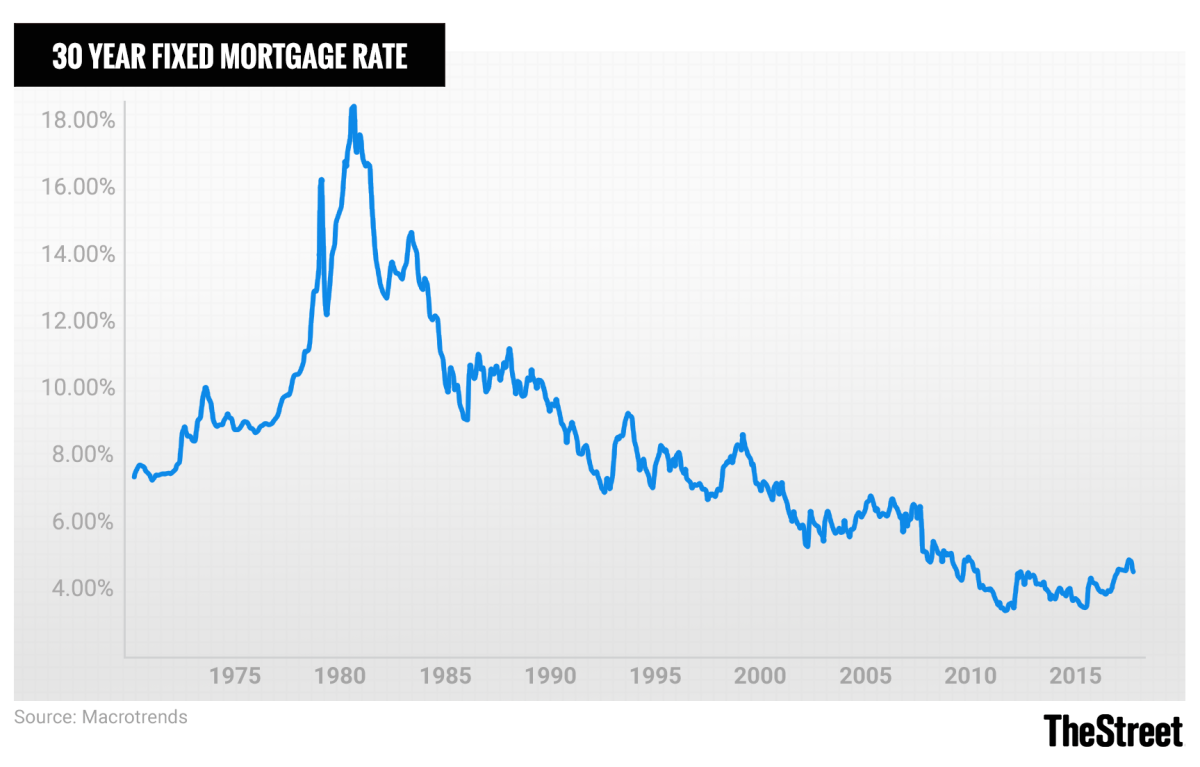
Historical Trends in Mortgage Interest Rates
Looking back at historical data, we can see that mortgage interest rates have experienced periods of highs and lows. For example, in the 1980s, rates reached double digits, while in recent years, they have been relatively low. These trends are influenced by various economic factors, such as inflation rates, central bank policies, and global market conditions.
Factors Contributing to Fluctuations in Mortgage Rates
Fluctuations in mortgage rates can be attributed to a variety of factors, including changes in the economy, housing market conditions, and investor sentiment. For instance, when the economy is strong, rates may rise as demand for loans increases. On the other hand, during economic downturns, rates may drop to stimulate borrowing and spending.
Current Market Conditions and Forecasts for Future Mortgage Rates
As of now, the mortgage market is experiencing historically low rates due to the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, forecasts suggest that rates may start to rise in the coming years as the economy recovers and inflation picks up. It’s essential for potential homebuyers to stay informed about these trends and consider locking in a rate while they are still favorable.