What is Student Loan Consolidation?

Student loan consolidation is the process of combining multiple student loans into a single loan with one monthly payment. This can be done through a direct consolidation loan from the federal government or by refinancing with a private lender.
Types of Student Loans that can be Consolidated
- Federal student loans: such as Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and PLUS Loans.
- Private student loans: loans obtained from private lenders or financial institutions.
Benefits of Consolidating Student Loans
- Simplified Repayment: Consolidating multiple loans into one can streamline the repayment process and make it easier to manage.
- Lower Monthly Payments: By extending the repayment term, borrowers may be able to reduce their monthly payments.
- Potential for Lower Interest Rates: Consolidating can also lead to a lower overall interest rate, saving money over the life of the loan.
- Opportunity for Loan Forgiveness: Some consolidation options may make borrowers eligible for loan forgiveness programs.
Eligibility Criteria

When it comes to student loan consolidation, there are specific eligibility criteria that borrowers need to meet in order to qualify for this financial option. Lenders consider various factors when determining if a borrower is eligible for consolidation, whether it’s for federal or private student loans.
Federal Student Loan Consolidation
- To be eligible for federal student loan consolidation, borrowers must have federal student loans that are in repayment or in their grace period.
- Borrowers must have a minimum amount of eligible loans to consolidate, typically ranging from $5,000 to $7,500.
- Eligible federal loans for consolidation include Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans, PLUS Loans, and more.
- Borrowers must not be in default on their federal student loans to qualify for consolidation.
Private Student Loan Consolidation
- For private student loan consolidation, lenders often consider the borrower’s credit score and income to determine eligibility.
- Borrowers with a good credit score and stable income are more likely to be eligible for private loan consolidation.
- Some lenders may require a minimum loan amount to be eligible for consolidation, which can vary depending on the lender.
- Unlike federal consolidation, private lenders may offer variable interest rates based on the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Pros and Cons
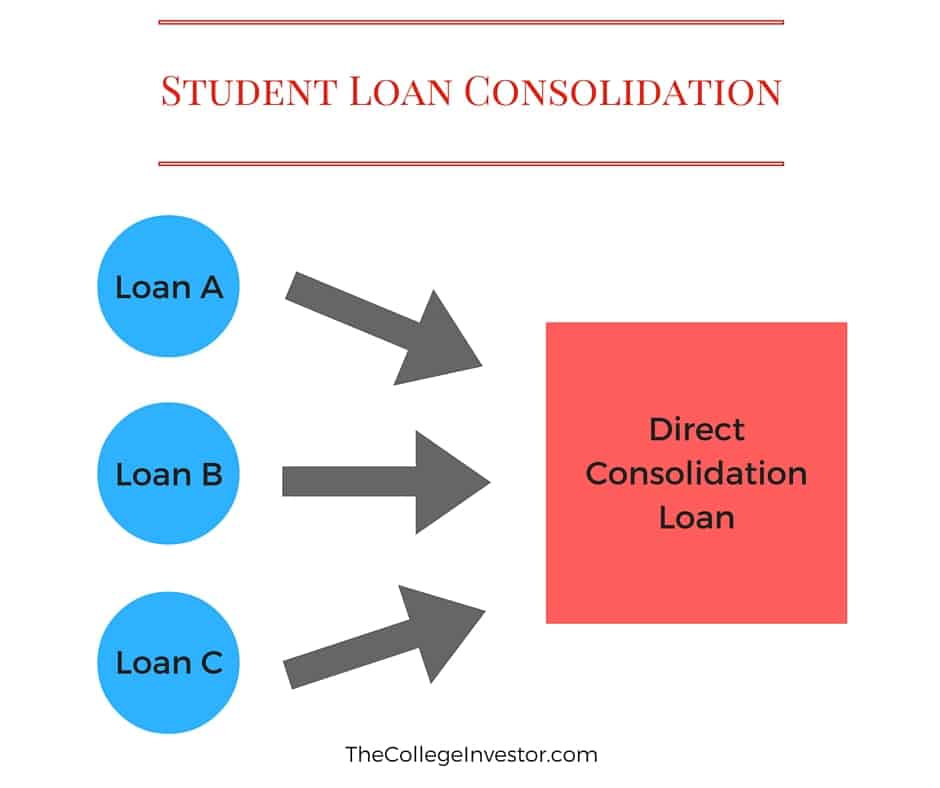
When considering student loan consolidation, it is essential to weigh both the advantages and disadvantages before making a decision. Here are some key points to consider:
Advantages of Student Loan Consolidation:
- Lower Monthly Payments: By consolidating multiple loans into one, you may be able to secure a lower monthly payment, making it easier to manage your finances.
- Fixed Interest Rate: Consolidation can provide the benefit of a fixed interest rate, which can protect you from potential rate increases in the future.
- Simplified Repayment: With just one loan to manage, you can streamline your repayment process and avoid the hassle of multiple due dates and payment amounts.
- Potential for Loan Forgiveness: Some consolidation programs offer forgiveness options after a certain number of on-time payments, which can be a significant advantage for borrowers.
Drawbacks of Student Loan Consolidation:
- Loss of Benefits: Consolidating federal loans into a private consolidation loan may result in the loss of certain borrower benefits such as income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness options.
- Extended Repayment Term: While lower monthly payments can be advantageous, extending the repayment term through consolidation may result in paying more interest over time.
- Potential for Higher Interest Rates: Depending on the terms of the consolidation loan, you may end up with a higher interest rate than what you had on your original loans.
- Limited Eligibility: Not all loans are eligible for consolidation, so it’s important to check if your loans qualify before proceeding.
Tips for Weighing the Pros and Cons:
- Evaluate Your Financial Situation: Consider your current financial status, future goals, and overall debt burden to determine if consolidation is the right choice for you.
- Compare Rates and Terms: Shop around and compare offers from different lenders to ensure you are getting the best possible terms for your consolidation loan.
- Consider Future Plans: Think about how consolidation will impact your long-term financial goals and whether the benefits outweigh the potential drawbacks in your specific situation.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you’re unsure about whether consolidation is right for you, consider consulting a financial advisor or student loan expert for personalized guidance.
Application Process
When applying for student loan consolidation, it is essential to follow a step-by-step process to ensure a smooth and successful application. Below is a detailed guide on how to navigate through the application process, including required documents and common mistakes to avoid.
Step 1: Gather Required Documents
- Personal identification (driver’s license, passport, or state ID)
- Social Security number
- Proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns, or W-2 forms)
- List of current outstanding student loans
- Loan account information
Step 2: Choose a Consolidation Program
- Research and compare different consolidation programs to find the one that best fits your financial situation.
- Consider the interest rates, repayment terms, and any additional benefits offered by each program.
- Contact the chosen program to inquire about the application process and any specific requirements.
Step 3: Complete the Application
- Fill out the consolidation application form accurately and completely.
- Double-check all information provided to avoid delays in processing.
- Submit the application before the deadline to ensure timely consolidation of your student loans.
Step 4: Review and Sign the Agreement
- Review the terms and conditions of the consolidation agreement carefully.
- Ensure you understand the new repayment plan, interest rate, and any other changes resulting from consolidation.
- Sign the agreement to proceed with the consolidation process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Providing inaccurate or incomplete information on the application form.
- Missing the deadline for submission of documents and application.
- Not reviewing the terms and conditions of the consolidation agreement thoroughly.
- Ignoring communication from the consolidation program regarding additional requirements or updates.