What is Risk Tolerance Assessment?

Risk tolerance assessment is a process used to evaluate an individual’s or organization’s willingness and ability to take on risks in various investment or decision-making scenarios. It helps determine the level of risk that a person or entity is comfortable with and can handle.
Assessing risk tolerance is crucial in making informed financial decisions, as it ensures that investments align with the individual’s goals, time horizon, and overall financial situation. It also helps in managing expectations and setting realistic objectives.
Importance of Assessing Risk Tolerance
Assessing risk tolerance is essential for creating a well-balanced investment portfolio that matches the individual’s risk profile. It helps in avoiding investments that are too risky or too conservative, leading to suboptimal returns or unnecessary exposure to market volatility.
- Age: Younger individuals may have a higher risk tolerance as they have more time to recover from potential losses.
- Financial goals: Short-term financial goals may require a more conservative approach, while long-term goals may benefit from a higher risk tolerance.
- Income stability: Individuals with stable income streams may be more willing to take on higher risks compared to those with fluctuating incomes.
- Knowledge and experience: Experienced investors may have a higher risk tolerance due to their understanding of market dynamics and investment strategies.
Methods for Assessing Risk Tolerance
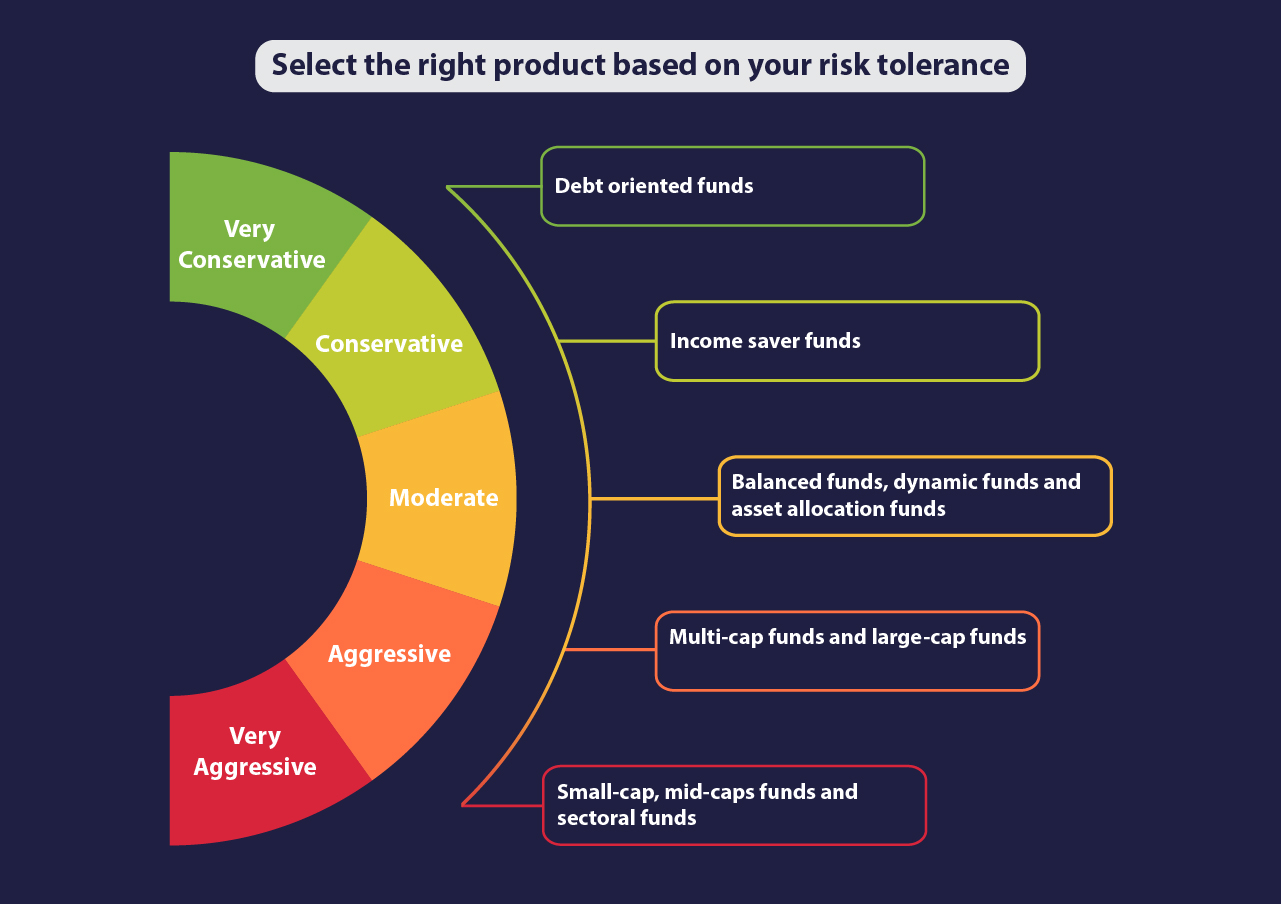
Assessing risk tolerance is crucial in financial planning to ensure that investments align with an individual’s comfort level with risk. There are various methods used to evaluate risk tolerance, each with its own set of pros and cons. Let’s explore some common approaches and compare quantitative and qualitative methods.
Quantitative Approaches
Quantitative methods involve using numerical data and calculations to determine an individual’s risk tolerance. This can include questionnaires that assign a numerical value to responses or formulas that analyze financial goals and risk capacity.
- Pros:
- Provides a clear, measurable result.
- Offers a structured approach to evaluating risk tolerance.
- Cons:
- May oversimplify complex risk attitudes.
- Relies heavily on numerical data, potentially missing emotional aspects of risk tolerance.
Qualitative Approaches
Qualitative methods focus on understanding an individual’s risk tolerance through open-ended questions, discussions, and scenarios. This approach delves into the emotional and psychological aspects of risk perception.
- Pros:
- Captures nuances and subtleties of risk attitudes.
- Allows for a more personalized assessment.
- Cons:
- Subjective nature may lead to inconsistent results.
- Difficult to quantify and compare across individuals.
Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches
When comparing quantitative and qualitative approaches to risk tolerance assessment, it is essential to consider the trade-offs between objectivity and subjectivity. While quantitative methods provide a numerical output for easy comparison, qualitative approaches offer a deeper understanding of an individual’s risk mindset. Combining both methods can result in a more comprehensive assessment that considers both the rational and emotional aspects of risk tolerance.
Factors Influencing Risk Tolerance

Various factors play a crucial role in determining an individual’s risk tolerance, shaping their approach to investment decisions and financial strategies.
Age
Age is a significant factor influencing risk tolerance. Younger individuals often have a higher risk tolerance as they have more time to recover from any potential losses. On the other hand, older individuals nearing retirement may have a lower risk tolerance to preserve their wealth.
Financial Situation
An individual’s financial situation, including income, savings, debts, and overall wealth, can impact their risk tolerance. Those with stable finances and significant savings may be more willing to take risks, while those facing financial constraints may prefer safer investment options.
Investment Goals
Investment goals, such as saving for retirement, purchasing a home, or funding education, can influence risk tolerance. Short-term goals may lead to a lower risk tolerance, while long-term goals might allow for more risk-taking to potentially achieve higher returns.
Psychological Aspects
Psychological factors, such as fear, overconfidence, and loss aversion, can significantly impact risk tolerance. Fear of loss may lead to a lower risk tolerance, while overconfidence can result in excessive risk-taking. Understanding these psychological aspects is essential in managing risk effectively.
Importance of Risk Tolerance Assessment in Financial Planning
Risk tolerance assessment plays a crucial role in financial planning as it helps individuals and investors make informed decisions about their investments based on their willingness and ability to take risks. By understanding one’s risk tolerance, financial planners can tailor investment strategies that align with their clients’ goals and preferences.
How Risk Tolerance Assessment Informs Financial Decision-Making
- Risk tolerance assessment helps investors understand their comfort level with risk and volatility, enabling them to make decisions that are in line with their financial objectives.
- It allows financial planners to recommend suitable investment options that match the risk profile of their clients, ensuring a balanced and diversified portfolio.
- By knowing their risk tolerance, individuals can avoid making impulsive decisions during market fluctuations, leading to more disciplined and strategic investment choices.
Examples of Risk Tolerance Assessment in Portfolio Construction
- Investors with a high risk tolerance may have a more aggressive investment portfolio with a higher allocation to equities and alternative investments.
- On the other hand, individuals with a low risk tolerance may opt for a more conservative approach, with a focus on fixed-income securities and lower-volatility assets.
- Based on the risk tolerance assessment, financial planners can adjust the asset allocation and investment mix to achieve the desired risk-return balance.
The Role of Risk Tolerance Assessment in Long-Term Financial Planning
- Understanding risk tolerance is essential for long-term financial planning as it helps individuals set realistic financial goals and expectations.
- By aligning investment strategies with risk tolerance, investors can stay committed to their long-term financial objectives even during market uncertainties.
- Regular review and reassessment of risk tolerance ensure that financial plans remain relevant and adaptable to changing circumstances and goals over time.