Definition of Secured vs. Unsecured Loans

Secured loans are loans that are backed by collateral, such as a car or a house. In the event that the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender can seize the collateral to recoup their losses. On the other hand, unsecured loans do not require any collateral and are based solely on the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Role of Collateral in Securing a Loan
Collateral acts as a form of security for the lender in case the borrower fails to repay the loan. It provides assurance that the lender will be able to recover their funds by selling the collateral if necessary. This lowers the risk for the lender, allowing them to offer lower interest rates on secured loans compared to unsecured loans.
Risks Associated with Secured and Unsecured Loans
- Secured Loans:
- Lower interest rates due to the collateral provided.
- Risk of losing the collateral if unable to repay the loan.
- Higher loan amounts can be obtained due to reduced risk for the lender.
- Unsecured Loans:
- Higher interest rates as there is no collateral backing the loan.
- Approval based solely on creditworthiness, which can be challenging for some borrowers.
- Lower loan amounts typically offered compared to secured loans.
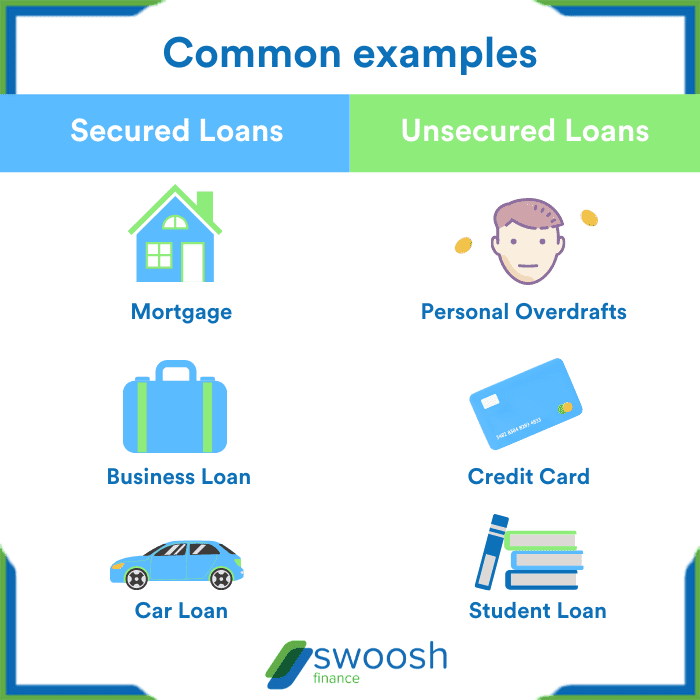
Types of Collateral for Secured Loans
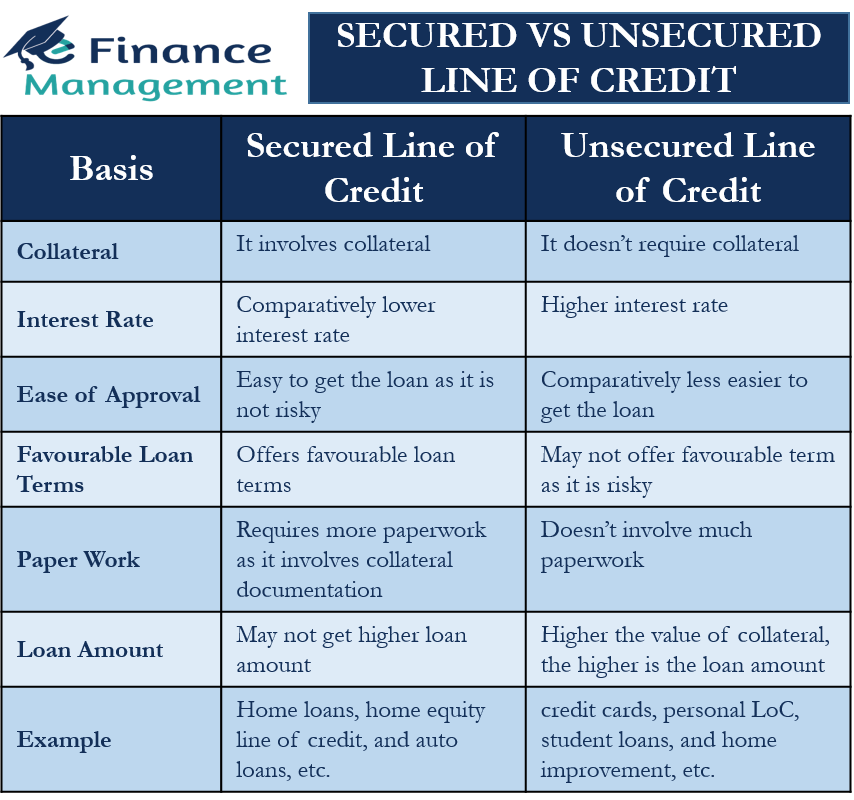
When applying for a secured loan, lenders often require collateral to mitigate the risk of default. Collateral serves as a form of security for the lender, ensuring that they have a way to recoup their losses if the borrower fails to repay the loan. Here are some common types of collateral accepted for secured loans:
Real Estate
Real estate properties such as homes, land, or commercial buildings are frequently used as collateral for secured loans. The value of the property is assessed to determine the loan amount that can be granted.
Vehicle
Cars, trucks, motorcycles, boats, or other types of vehicles can also be used as collateral for loans. The lender may take possession of the vehicle if the borrower defaults on the loan.
Investments
Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or other investment accounts can be pledged as collateral for a secured loan. The value of the investments is considered when determining the loan terms.
Jewelry and Valuables
Precious items such as jewelry, artwork, antiques, or other valuables can be used as collateral for a loan. The lender may require an appraisal to determine the value of these items.
Equipment
Businesses may use equipment, machinery, or inventory as collateral for loans. The lender may seize these assets in case of loan default.
Accounts Receivable
Companies can use their accounts receivable as collateral for financing. This involves pledging the money owed by customers as security for the loan.
Interest Rates and Terms
When it comes to secured and unsecured loans, the interest rates and terms can vary significantly based on the type of loan and the borrower’s credit profile. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
Interest Rates
Interest rates for secured loans are typically lower than those for unsecured loans. This is because secured loans are backed by collateral, which reduces the risk for the lender. In contrast, unsecured loans do not require collateral, making them riskier for lenders and resulting in higher interest rates.
Loan Terms
The terms of a loan, including the repayment period and monthly payments, can also differ between secured and unsecured loans. Secured loans often have longer repayment periods, allowing borrowers more time to pay off the loan. On the other hand, unsecured loans may have shorter terms and higher monthly payments due to the increased risk for the lender.
Credit Scores Impact
Credit scores play a significant role in determining the interest rates for both secured and unsecured loans. Borrowers with higher credit scores are typically offered lower interest rates, as they are considered less risky by lenders. On the other hand, borrowers with lower credit scores may face higher interest rates or even struggle to qualify for certain loans.
Overall, understanding how interest rates and terms differ between secured and unsecured loans can help borrowers make informed decisions and choose the option that best fits their financial needs and circumstances.
Approval Process and Application Requirements
When it comes to securing a loan, whether it’s a secured or unsecured one, the approval process and application requirements can vary significantly. Let’s delve into the details to understand the differences.
Approval Process for Secured Loans vs. Unsecured Loans
Secured loans typically have a more straightforward approval process compared to unsecured loans. This is because secured loans are backed by collateral, reducing the risk for lenders. The collateral provides a form of security for the loan, making it less risky for the lender to approve the application. On the other hand, unsecured loans do not require collateral, which can make them harder to qualify for, as the lender relies solely on the borrower’s creditworthiness.
Application Requirements for Securing a Loan
For secured loans, the primary requirement is collateral. The collateral can be in the form of real estate, vehicles, investments, or other valuable assets. The value of the collateral will determine the loan amount that can be approved. In contrast, unsecured loans do not require collateral. Instead, lenders will assess the borrower’s credit score, income, employment status, and other financial factors to determine eligibility.
Documentation Needed for Each Type of Loan
When applying for a secured loan, borrowers will need to provide documentation related to the collateral being used. This may include property deeds, vehicle titles, investment statements, or any other proof of ownership. Additionally, borrowers will need to submit standard financial documents such as income verification and credit history. For unsecured loans, documentation requirements typically focus on the borrower’s financial stability, including proof of income, employment verification, and a good credit score.