Introduction to Dividend Investing

Dividend investing is a strategy where investors focus on purchasing stocks that pay out regular dividends. These dividends are a portion of the company’s profits distributed to shareholders as a reward for investing in the company.
Benefits of Dividend Investing
- Stable Income: Dividend investing provides a steady stream of income for investors, making it a popular choice for those seeking regular cash flow.
- Long-Term Growth: Companies that consistently pay dividends tend to be financially stable and have the potential for long-term growth.
- Reinvestment Opportunities: Investors can reinvest their dividends to purchase more shares, leading to compound growth over time.
Key Reasons Why Investors Choose Dividend Investing
- Income Generation: Many investors rely on dividends as a source of passive income, especially during retirement.
- Historical Performance: Dividend-paying stocks have historically outperformed non-dividend-paying stocks, providing investors with attractive returns.
- Dividend Growth: Companies that increase their dividends regularly signal strong financial health and a commitment to rewarding shareholders.
Types of Dividend Investing Strategies
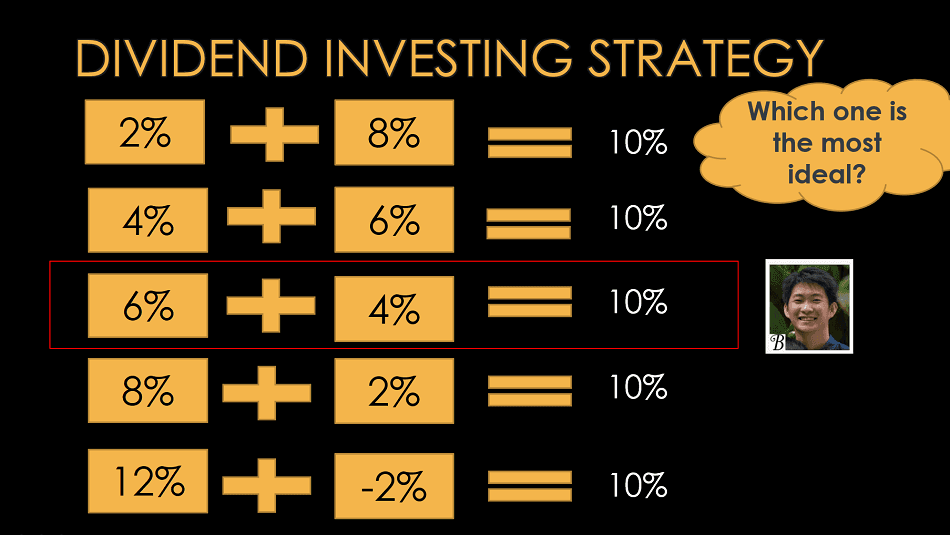
Dividend investing strategies can vary based on the goals and preferences of investors. Three common types of dividend investing strategies include dividend growth, high dividend yield, and dividend value. Each strategy has its own unique characteristics and benefits.
Dividend Growth Strategy
The dividend growth strategy focuses on investing in companies that consistently increase their dividend payouts over time. These companies are typically stable and have strong growth potential. Investors who follow this strategy prioritize companies with a history of steady dividend increases, as they believe this is a sign of financial health and long-term success.
Examples of companies that align with the dividend growth strategy include Johnson & Johnson, Coca-Cola, and Procter & Gamble. These companies have a track record of raising their dividends annually, making them attractive investments for dividend growth investors.
High Dividend Yield Strategy
The high dividend yield strategy involves investing in companies that offer a high dividend yield relative to their stock price. Investors following this strategy seek out companies that pay a significant portion of their earnings as dividends. While these companies may not always have the same level of dividend growth as others, they provide a steady stream of income through their high dividend payments.
Companies like AT&T, Verizon, and ExxonMobil are examples of companies that align with the high dividend yield strategy. These companies are known for their high dividend yields, making them popular choices for investors looking for consistent income.
Dividend Value Strategy
The dividend value strategy combines elements of both dividend growth and high dividend yield strategies. Investors following this strategy look for companies that not only have a history of increasing dividends but also trade at an attractive valuation. These companies are considered undervalued by the market, presenting an opportunity for capital appreciation in addition to dividend income.
Companies such as Microsoft, Apple, and Visa are examples of companies that align with the dividend value strategy. These companies have demonstrated strong dividend growth potential while also being viewed as undervalued investments in the market.
By understanding the different types of dividend investing strategies and the companies that align with each strategy, investors can tailor their investment approach to meet their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Factors to Consider in Dividend Investing

Before delving into dividend investing, it is crucial to consider various factors that can impact your investment decisions. These factors play a significant role in determining the success of your dividend investment strategy. Let’s explore some of the key considerations below.
Dividend Yield
The dividend yield is a critical metric that investors use to evaluate the attractiveness of a dividend-paying stock. It is calculated by dividing the annual dividend payment by the stock price. A higher dividend yield indicates a higher return on investment. However, a very high dividend yield could be a red flag, signaling that the stock price has fallen significantly and the dividend may not be sustainable.
Payout Ratio
The payout ratio is another essential factor to consider before selecting a dividend investment. This ratio represents the percentage of earnings that a company pays out to shareholders in the form of dividends. A lower payout ratio indicates that the company has room to increase dividends in the future or reinvest in the business for growth. On the other hand, a high payout ratio may suggest that the company is paying out most of its earnings as dividends, leaving little room for future dividend growth or reinvestment.
Dividend Consistency
Consistency in dividend payments is key for income investors seeking a reliable source of passive income. Companies with a history of consistent dividend payments demonstrate financial stability and shareholder-friendly policies. Investors should look for companies that have a track record of maintaining or increasing dividends over time, even during economic downturns.
Market Conditions
Market conditions can significantly influence dividend investing decisions. During periods of economic uncertainty or market volatility, companies may face challenges in maintaining dividend payments. It is essential for investors to assess the overall market environment, industry trends, and the financial health of the companies in which they plan to invest. Understanding how market conditions can impact dividend stocks will help investors make informed decisions and navigate potential risks.
Building a Diversified Dividend Portfolio
When it comes to building a diversified dividend portfolio, it’s important to carefully consider various factors to ensure a balanced and effective investment strategy. By incorporating different dividend investing strategies and organizing asset allocation thoughtfully, investors can optimize their portfolio for long-term success.
Designing a Diversified Portfolio
Creating a diversified dividend portfolio involves selecting a mix of dividend-paying stocks across different sectors and industries. By spreading investments across various companies, investors can reduce the risk associated with any single stock or sector underperforming. This diversification can help protect the portfolio from market volatility and economic downturns.
- Consider including dividend aristocrats: These are companies with a long history of consistently increasing their dividends year over year. They are often viewed as stable and reliable investments.
- Include dividend growth stocks: These are companies that may not have a long dividend history but show strong potential for increasing dividends in the future. They can provide both income and growth opportunities.
- Explore high-yield dividend stocks: These stocks offer higher dividend yields but may come with higher risk. It’s important to balance high-yield investments with more stable dividend-paying stocks to manage risk effectively.
Organizing Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of building a diversified dividend portfolio. Investors should determine the percentage of their portfolio allocated to different types of dividend investments based on their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.
For example, conservative investors may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to dividend aristocrats for stability, while more aggressive investors may focus on high-yield dividend stocks for higher potential returns.
Tips for Balancing Risk and Return
Balancing risk and return in a dividend portfolio requires careful consideration of various factors, including diversification, investment goals, and market conditions. Here are some tips to help investors navigate this balance:
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
- Monitor the performance of individual stocks and sectors within your portfolio to identify any potential risks or opportunities.
- Diversify across asset classes, including bonds, REITs, and other dividend-paying investments, to further reduce risk and enhance potential returns.