Introduction to Building a Financial Portfolio

A financial portfolio refers to a collection of investments held by an individual or entity. It is a strategic approach to managing assets, aiming to achieve financial goals and mitigate risks.
Diversification is a crucial element in a financial portfolio as it helps spread risk across different types of investments. By diversifying, investors can reduce the impact of a negative event on any single investment.
The Key Components of a Well-Rounded Financial Portfolio
When building a well-rounded financial portfolio, it is important to consider the following key components:
- Equities: Investing in stocks of publicly traded companies can offer capital appreciation potential.
- Bonds: Fixed-income securities provide a steady income stream and can act as a hedge against market volatility.
- Real Estate: Real estate investments can provide diversification and potential for long-term growth through rental income and property value appreciation.
- Commodities: Investing in commodities such as gold, silver, or oil can help hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities managed by professional fund managers.
- ETFs: Exchange-traded funds offer diversification like mutual funds but trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks.
Types of Investment Options
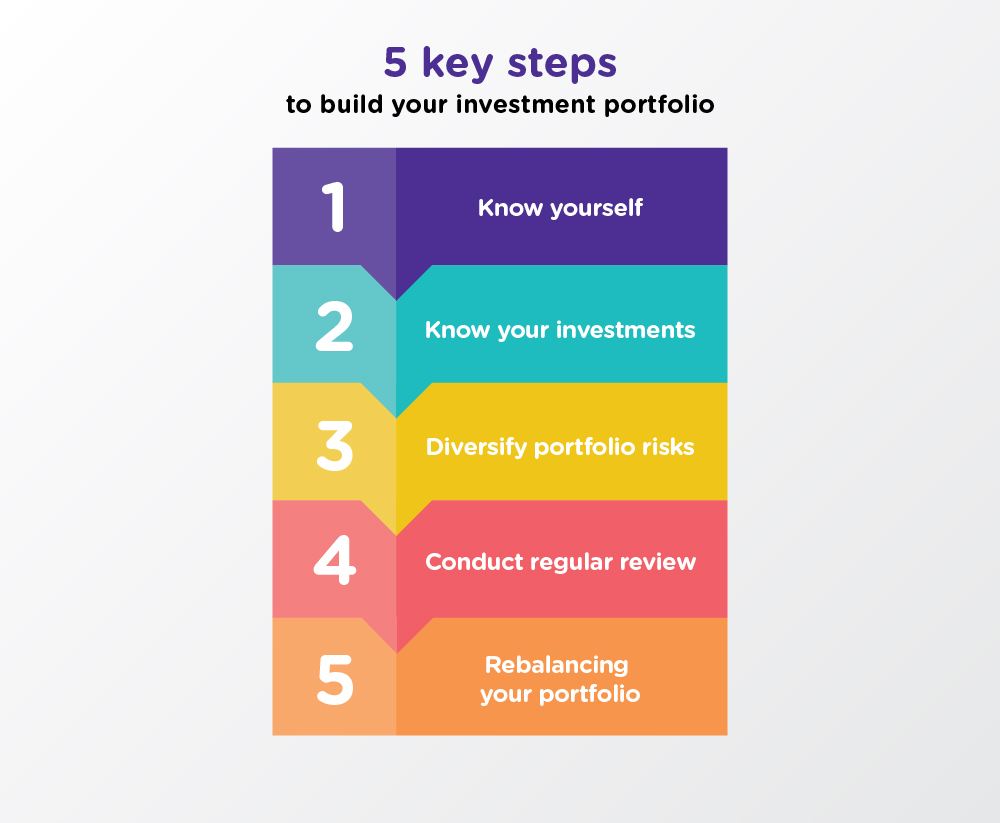
Investing is a crucial part of building a financial portfolio. There are various types of investment options available, each with its own risk and return profiles. Let’s explore some of the popular choices investors consider:
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for high returns. However, they also come with a higher level of risk due to market volatility and company-specific factors.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They are considered less risky than stocks but typically offer lower returns. Bonds can provide a steady income stream through interest payments.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They offer diversification and professional management but come with management fees.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
ETFs are similar to mutual funds but trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They combine the diversification of mutual funds with the flexibility of trading stocks. ETFs also have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds.
Alternative Investments
Alternative investments include assets like real estate, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. These investments can provide diversification beyond traditional stocks and bonds. However, they often come with higher risks and may lack liquidity.
Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon when choosing among these investment options to build a well-rounded financial portfolio.
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation is a crucial concept in building a successful financial portfolio. It involves dividing your investments among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents, to achieve a balance between risk and return. By diversifying your investments across various asset classes, you can reduce the overall risk of your portfolio while potentially maximizing returns.
Aggressive Asset Allocation
Aggressive asset allocation involves investing a larger portion of your portfolio in high-risk, high-return investments such as stocks. This strategy is suitable for investors with a high risk tolerance and a long investment horizon. While aggressive asset allocation has the potential for higher returns, it also comes with increased volatility and the risk of significant losses.
Moderate Asset Allocation
Moderate asset allocation strikes a balance between risk and return by diversifying investments across different asset classes. This strategy is suitable for investors with a moderate risk tolerance who seek a balance between growth and stability. Moderate asset allocation typically involves a mix of stocks, bonds, and cash equivalents to reduce overall portfolio risk.
Conservative Asset Allocation
Conservative asset allocation prioritizes capital preservation and stability over high returns. Investors with a low risk tolerance often opt for this strategy, allocating a larger portion of their portfolio to less volatile investments such as bonds and cash equivalents. While conservative asset allocation may offer lower returns compared to aggressive strategies, it provides more stability and protection against market downturns.
Determining the right asset allocation for your financial goals and risk tolerance is essential. It’s important to regularly review and adjust your asset allocation as your financial situation and goals change to ensure your portfolio remains aligned with your objectives.
Risk Management Techniques
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/building-complete-financial-portfolio-357968-color-FINAL2-86933638b6844aa296049011de61d7fb.png)
Risk management techniques are crucial to safeguard a financial portfolio from market volatility. By employing various strategies, investors can mitigate potential losses and protect their investments.
Hedging Strategies
Hedging strategies like options, futures, or stop-loss orders play a key role in risk management. These tools allow investors to limit their exposure to market fluctuations and protect their portfolio from sudden downturns.
Diversification
Diversification is another effective risk management technique. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors can reduce the impact of a single market event on their overall portfolio.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
Dollar-cost averaging involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This strategy helps investors avoid making emotional decisions based on short-term market movements and ensures a more consistent approach to investing over time.
Asset Rebalancing
Asset rebalancing involves periodically reviewing and adjusting the allocation of assets in a portfolio to maintain the desired risk level. By selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming ones, investors can realign their portfolio with their long-term investment goals.
Monitoring and Rebalancing
Regularly monitoring and rebalancing a financial portfolio is crucial to ensure that it remains aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By keeping a close eye on your investments and making necessary adjustments, you can optimize your portfolio’s performance and minimize potential risks.
Key Indicators for Assessing Investment Performance
- Rate of Return: Monitor the overall performance of your investments by calculating the rate of return. This will give you a clear picture of how well your portfolio is performing.
- Asset Allocation: Check if the distribution of assets in your portfolio aligns with your target asset allocation. Rebalancing may be needed if certain assets have deviated significantly from their original allocation.
- Risk Level: Assess the overall risk level of your portfolio and ensure it matches your risk tolerance. Adjustments may be necessary if the risk is too high or too low.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about market trends and economic conditions that may impact your investments. Make adjustments accordingly to capitalize on opportunities or mitigate risks.
Rebalancing a Portfolio
To rebalance your portfolio and maintain the desired asset allocation, follow these steps:
- Evaluate Current Allocation: Review the current distribution of assets in your portfolio and identify any deviations from your target allocation.
- Determine Rebalancing Strategy: Decide on the rebalancing strategy based on the extent of deviation and your investment goals. This could involve selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming assets to bring the portfolio back in line with your targets.
- Implement Rebalancing: Execute the rebalancing by buying or selling assets as per the decided strategy. Ensure that the transaction costs and tax implications are taken into consideration.
- Monitor Regularly: Continuously monitor your portfolio and make adjustments as needed to maintain the desired asset allocation over time.