Overview of Retirement Age Statistics
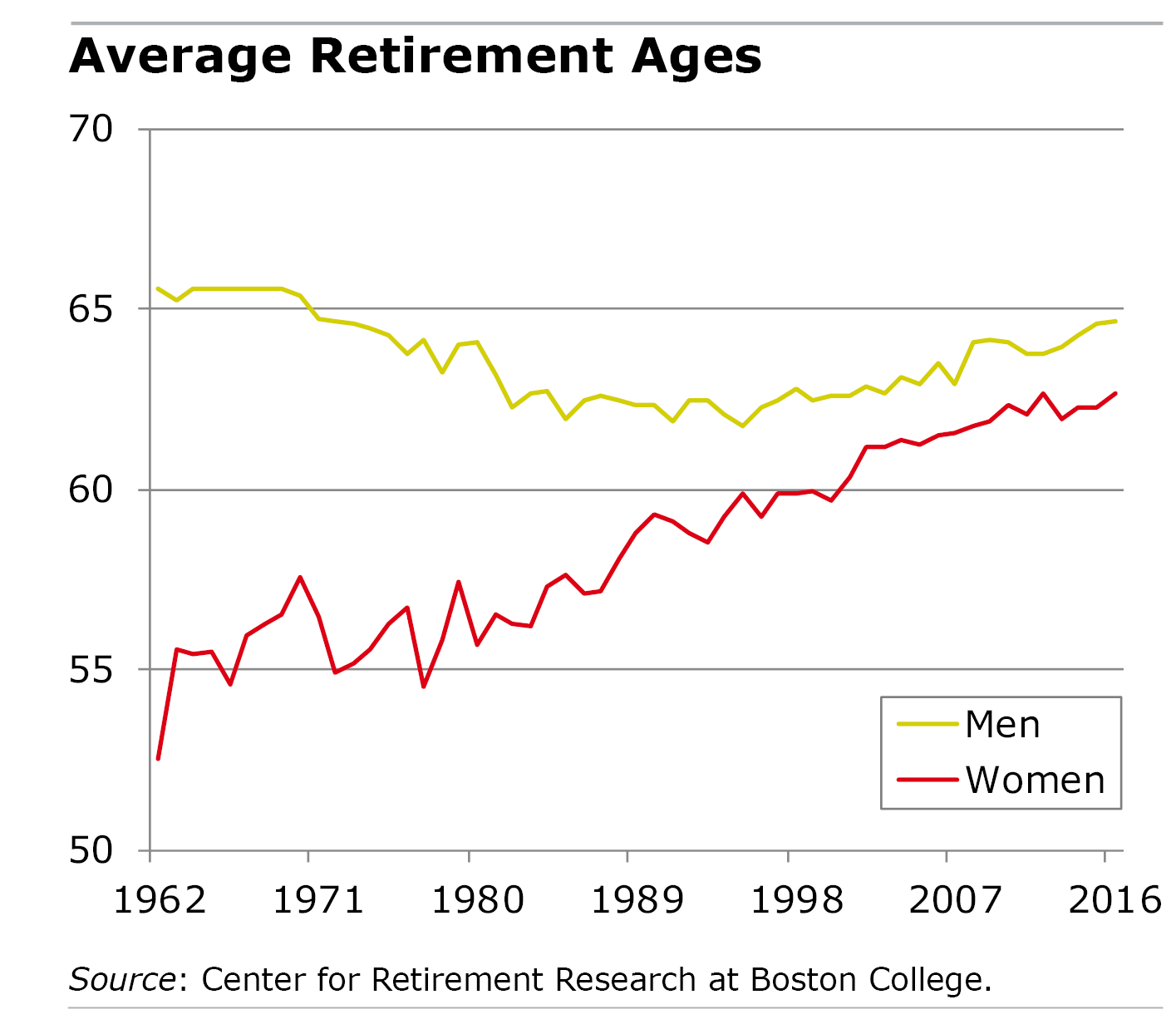
Retirement age statistics refer to the data and information related to the age at which individuals typically retire from the workforce. These statistics provide insights into trends, patterns, and demographics surrounding retirement decisions.
Retirement age statistics are crucial for policymakers and researchers to understand the impact of retirement on various aspects of society, such as labor force participation, social security programs, healthcare systems, and economic stability. By analyzing these statistics, policymakers can make informed decisions regarding retirement policies, benefits, and programs to address the evolving needs of an aging population.
Common Sources for Gathering Retirement Age Statistics Data
- National Surveys: Many countries conduct national surveys, such as the U.S. Census Bureau’s Current Population Survey (CPS), to collect data on retirement age trends and patterns.
- Social Security Administration: Data from the Social Security Administration provides valuable insights into retirement age trends, benefit claims, and demographic information.
- Research Studies: Academic research studies and reports often analyze retirement age statistics based on various datasets and methodologies.
- Employer Records: Some retirement age statistics are derived from employer records, such as pension plans and retirement benefit programs.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age
Retirement age is influenced by a variety of factors that can vary from country to country. These factors can include economic conditions, government policies, cultural norms, and individual preferences.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions play a significant role in determining retirement age. In countries with strong economies and stable job markets, individuals may choose to retire later to maximize their retirement savings. On the other hand, in countries facing economic challenges or high unemployment rates, individuals may be forced to retire earlier than planned due to financial constraints.
Government Policies
Government policies, such as retirement age laws and pension regulations, can also influence when individuals choose to retire. Some countries have mandatory retirement ages set by the government, while others offer incentives for individuals to work longer by providing increased benefits for delaying retirement.
Cultural Norms
Cultural norms and societal expectations can impact retirement age as well. In some cultures, there is a strong emphasis on continuing to work and contribute to society well into old age, leading individuals to retire later. In contrast, in cultures that prioritize leisure and family time, individuals may choose to retire earlier to enjoy their golden years.
Health and Longevity
The health and longevity of individuals can also play a role in determining retirement age. Advances in healthcare and increased life expectancy have allowed many people to live longer, healthier lives, leading some individuals to work past traditional retirement ages to stay active and engaged.
Global Retirement Age Trends
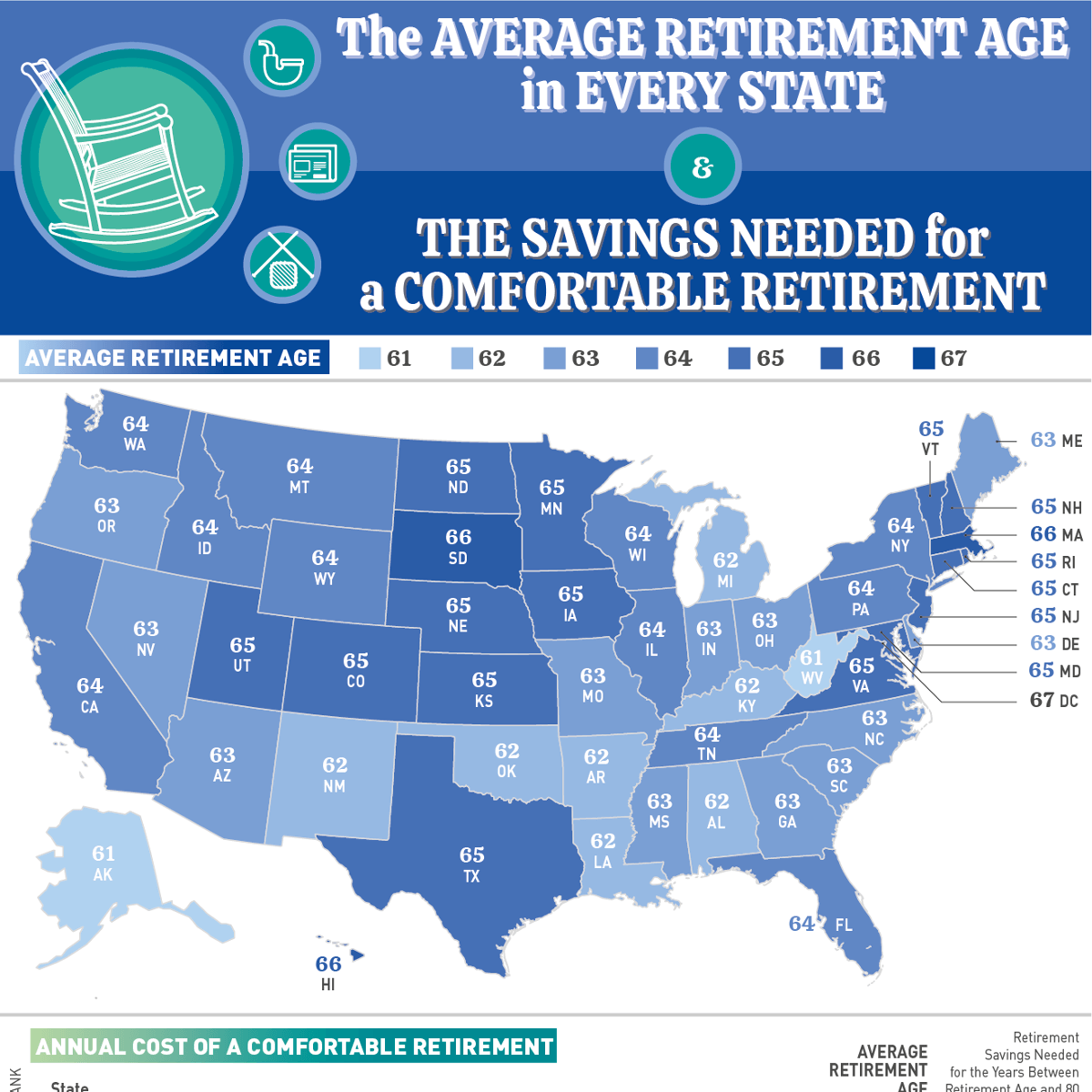
Retirement age trends vary significantly across different countries and regions worldwide. In recent years, there has been a noticeable shift in retirement age patterns, influenced by various socio-economic factors.
Evolution of Retirement Age
Over the past few decades, retirement age has gradually increased in many developed countries due to factors such as increased life expectancy, changing labor market dynamics, and financial sustainability of pension systems. This trend has led to individuals working longer before retiring.
Comparison between Developed and Developing Countries
Developed countries tend to have higher retirement ages compared to developing nations. This can be attributed to better access to healthcare, higher standards of living, and more robust pension schemes in developed economies. In contrast, developing countries often have lower retirement ages due to various factors like limited access to healthcare, lower life expectancies, and less comprehensive social security systems.
Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
Gender disparities in retirement age statistics reveal significant differences between men and women in when they retire. These variations can stem from a variety of factors that influence retirement decisions.
Reasons Behind Differences in Retirement Ages
There are several reasons behind the variations in retirement ages between men and women. One key factor is the gender pay gap, as women tend to earn less over their careers, resulting in smaller retirement savings. Additionally, women often take on caregiving responsibilities for children or elderly family members, leading to career breaks that can impact their retirement readiness. Societal norms and expectations may also play a role, with traditional gender roles influencing retirement decisions.
Policies and Initiatives Addressing Gender Disparities
Several policies and initiatives have been implemented to address gender disparities in retirement age. For example, some countries have introduced pension reforms to ensure equal access to retirement benefits for both genders. Workplace initiatives promoting gender equality, such as flexible working arrangements and parental leave policies, can also help women stay in the workforce longer and improve their retirement prospects.
Retirement Age Statistics by Occupation
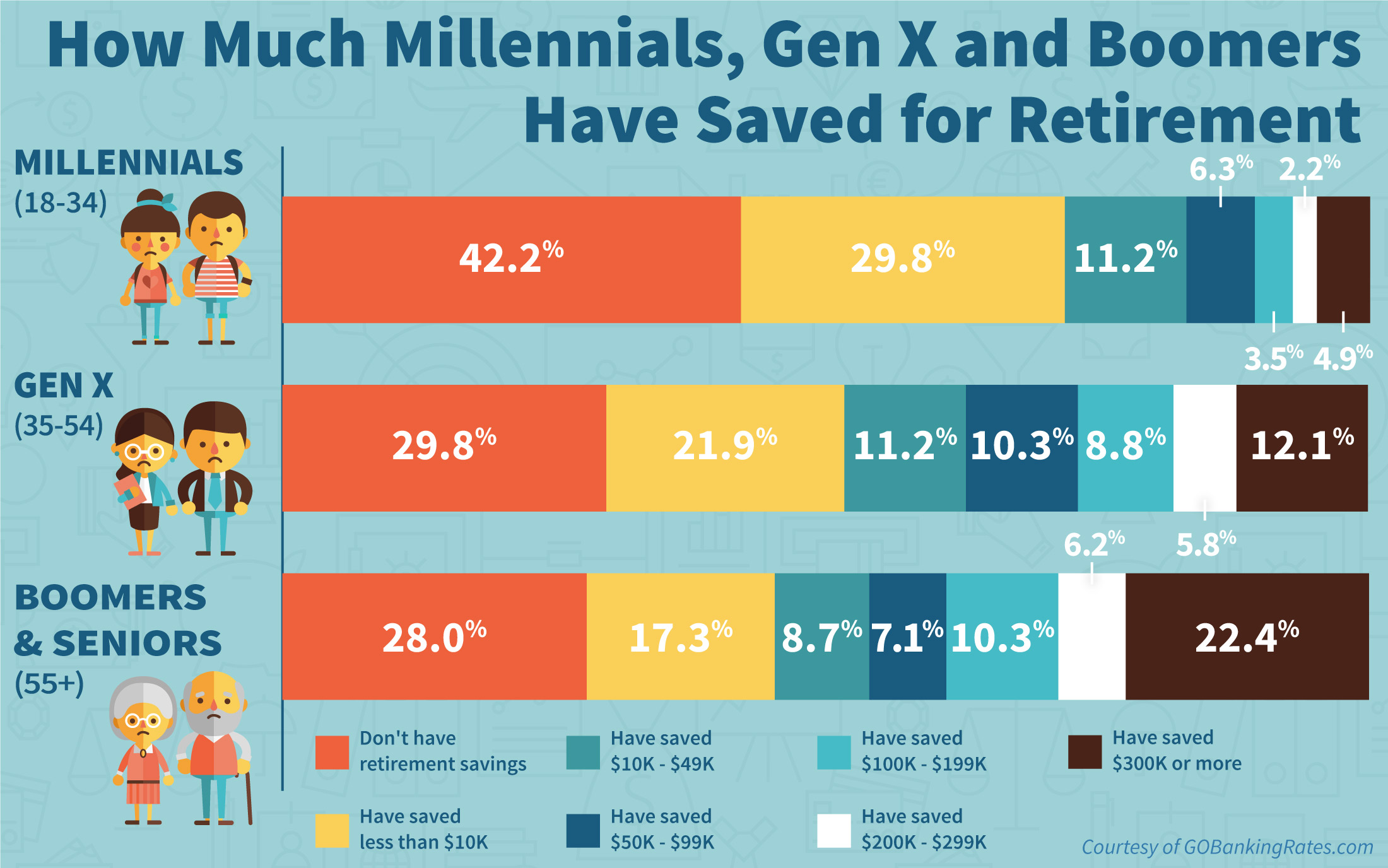
When it comes to retirement age, different occupations can have a significant impact on when individuals choose to retire. Factors such as job demands, physical labor, mental stress, and financial stability can all play a role in determining the retirement age for various professions.
Professions with Higher Retirement Ages
- University Professors: Due to tenure systems and a passion for teaching, university professors often retire later in life compared to other occupations.
- Medical Doctors: Physicians may continue working well into their 60s or even 70s due to the extensive training required and the desire to serve their patients.
- CEOs and Executives: Those in high-level executive positions may delay retirement to maintain their leadership roles and financial stability.
Professions with Lower Retirement Ages
- Construction Workers: The physical demands of this profession often lead to earlier retirement ages as individuals may not be able to continue the strenuous work as they age.
- Professional Athletes: Athletes in physically demanding sports typically retire in their 30s or 40s due to the physical toll of their careers.
- Artists and Performers: Some artists and performers may retire earlier due to the unpredictable nature of their careers and the need to make room for younger talents.
Impact of Occupation on Retirement Age
Occupation plays a crucial role in determining when individuals choose to retire. Those in physically demanding or high-stress professions may opt to retire earlier to prioritize their health and well-being. On the other hand, individuals in positions with flexible schedules or a passion for their work may continue working well into their later years. Ultimately, the occupation one chooses can significantly influence their retirement age decision.